|
METODORF.COM
Interactive Portal-Book of Self-Development Methods
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
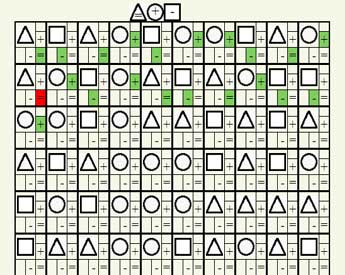
Pieron-Ruser test - online version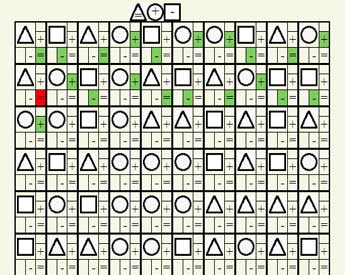 The Pieron-Ruser test, a variation of the well-known test called the Bourdon test, is used to measure the attentional potential of children and adults. With the help of Pierrene-Ruser’s test, you can measure attention such as: characteristics of voluntary attention, attention stability, switching levels and distribution of attention. It is necessary to fill the cells sequentially - from left to right, first the top line, and only then the line below. This online version of the test can give a rough estimate of the possibilities of your attention, for a more accurate result it is recommended to pass a professional test. Instructions for performing the Pieron-Ruser test:For filling 100 figures with appropriate signs, a limited time is given from 2 minutes for high school students and adults and up to 5 minutes for primary school children. In front of you you see 10 rows of 10 geometric shapes, in each of which you need to select the corresponding symbols, which are represented in the template - the top row of shapes filled with symbols. Your task is to fill in as much time as possible with the appropriate symbols in the allotted time. Remember or see which symbol should contain one or another figure and fill it.
Pieron-Ruser test theory: The study is conducted to verify concentration, stability, distribution, switching attention, as well as assessing the childs attention from 6 to 10 years. The calculation is made by two indicators - processing speed, calculated by the formula: V=N/10, and accuracy - according to the formula: K=(N-A)/N. Where N is the number of characters processed, and A is the average number of errors per line, calculated from the sum of the errors in the lines divided by the number of lines.
Sources: E.Yu. Brunner "Better than super-attention. Methods of diagnosis and psycho-correction." - Rostov-on-Don, "Phoenix", 2006. © Oleg Akvan metodorf.com Comment block No one has left comments here yet, be the first! Leave a comment:
Advertisement:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 2014 - 2026 Oleg Akvan metodorf.com
All rights reserved!
All rights reserved!